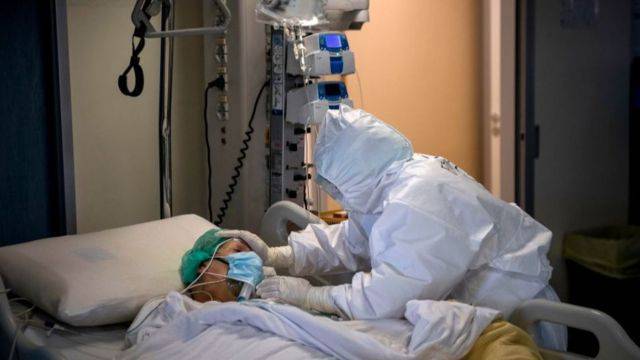
Under the title "Study: 60% of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients Suffer at Least One Symptom After 6 Months," the Emirates Today website reported on a French study showing that 60% of patients admitted to hospitals due to COVID-19 "still suffer from at least one symptom six months after infection," often fatigue, pain, or difficulty breathing. The study, conducted by the National Institute of Health and Medical Research and published in the journal "Clinical Microbiology and Infection," indicated that 25% of these patients exhibit "three or more symptoms," and 2% "were readmitted to the hospital."
The study followed a group of 1,137 patients to monitor their conditions after receiving hospital treatment. According to the study, follow-up health examinations conducted three and six months after hospital treatment for COVID-19 revealed that "among the most commonly reported ongoing clinical symptoms were feelings of significant fatigue, respiratory difficulties, and muscle and joint pain."
Researchers observed "a link between the severity of the illness at the outset and the persistence of symptoms over a long duration." They concluded that the presence of at least three ongoing symptoms six months after infection "was more common among individuals whose COVID-19 infection required admission to intensive care units compared to those admitted to regular care units, and among patients who exhibited more severe symptoms at the time of their hospital admission."
The study also revealed that while men were more likely to suffer serious complications, women appeared to be at a higher risk of experiencing long-lasting symptoms. The study emphasizes that the impact of long-term COVID-19 symptoms can sometimes be greater on both economic and social levels, as one-third of patients who reported symptoms six months post-infection and were engaged in professional activities at the time of their illness had not returned to work. The findings align with conclusions from several studies conducted in other countries in recent months.
It is estimated that 10% of COVID-19 patients with symptoms continue to experience lasting effects of "SARS-CoV-2," including individuals who were not hospitalized and those who experienced mild to moderate symptoms.