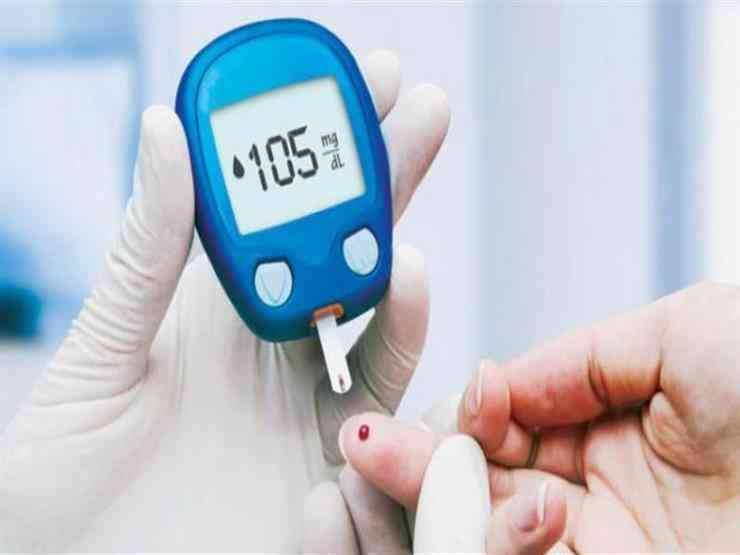
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type of diabetes, and prevention is possible and important, especially if you are at risk due to genetics or obesity. Preventing diabetes is absolutely essential and should never be delayed. Making some simple lifestyle changes now can help you avoid serious health complications from diabetes in the future. The latest diabetes prevention tips from the American Diabetes Association include:
**Exercise as Much as You Can**
There are several benefits to regular physical activity; exercising and walking regularly can help you:
- Shed excess weight.
- Lower blood sugar levels.
- Increase insulin sensitivity, helping to maintain normal blood sugar levels.
- Improve cardiovascular fitness.
Research shows that aerobic exercises and strength training help control diabetes, but the greatest benefit comes from a fitness program that incorporates both.
**Consume Plenty of Natural Fiber**
Fiber helps you:
- Reduce the risk of diabetes by improving blood sugar control.
- Lower the risk of heart disease.
- Improve weight loss by helping you feel full.
- Improve cholesterol management.
- Decrease the likelihood of colon cancer.
- Enhance bowel regularity.
Fiber-rich foods include fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
**Choose Whole Grains in Your Diet**
Whole grains, thanks to their fiber content, help reduce the risk of diabetes and maintain blood sugar levels.
Try to make at least half of the grains you consume whole grains in bread, pasta products, and many types of cereals, and look for the word "whole" on the package and among the first few items in the food ingredient list.
**Lose Excess Weight**
If you are overweight or obese, diabetes prevention may hinge entirely on losing weight. Every kilogram you lose can improve your health, and you may be surprised at the level of improvement. In one large study, the risk of developing diabetes decreased by almost 60 percent among participants who lost a small amount of weight—about 7 percent of their body weight—and exercised regularly.
**Avoid Processed Foods and Make Safer Choices**
Low-carbohydrate diets or diets based on the glycemic index and other diets can help with initial weight loss, but their effectiveness in preventing diabetes is unknown, as are their long-term effects. Instead of excluding certain foods strictly, such as white bread, processed meats, ready-made desserts, potatoes, rice, and artificial sweeteners, consider diversifying and controlling portion sizes as part of an overall healthy eating plan.
**When Should You Visit a Doctor?**
The American Diabetes Association recommends checking blood sugar levels in the following cases:
- If you are 45 years old or older and overweight.
- If you are younger than 45, overweight, and have one or more additional risk factors for type 2 diabetes—such as a sedentary lifestyle or a family history of diabetes.
Consult your doctor about any concerns you have regarding diabetes prevention, as they will commend your efforts and may offer further suggestions based on your medical history or other factors.