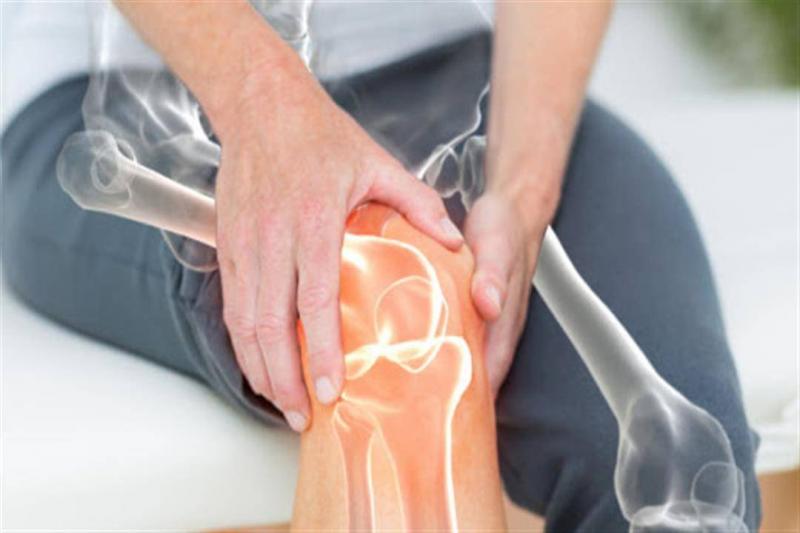
Osteoporosis mainly affects adults, particularly those in their mid-forties or older, causing inflammation, joint stiffness, and pain. Motion expert Lee Cartwright explained, "Osteoporosis begins by damaging the smooth cartilage lining of the joints, making movement difficult and causing pain and stiffness. As the cartilage surface becomes rougher and thinner, pressure increases on tendons and ligaments, potentially leading to swelling and the development of bone growth known as bone spurs." The loss of cartilage can lead to bones rubbing against each other, contributing to changes in joint shape and misalignment of bones. Common signs of osteoporosis include increased pain while walking and joint stiffness after movement, especially if you are over 45.
Here are seven preventive measures that can be taken to address this health issue:
- **Follow a Balanced Diet**: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals is essential for joint health. Dairy products like milk and cheese are excellent sources of calcium, which is crucial for joint health and bone mass building. Additionally, incorporating salmon and sardines, which are rich in vitamin D and Omega-3 fatty acids, helps maintain bone density and has anti-inflammatory properties that reduce the risk of bone loss.
- **Maintain a Healthy Weight**: Experts explain that excess weight puts additional pressure on joints, particularly the knees and hips. Therefore, losing weight can significantly reduce wear and tear on the joints.
- **Exercise Regularly**: Regular physical activity is essential for joint health, but it doesn’t have to be strenuous. Simple activities like walking or cycling for 10 to 30 minutes help strengthen the muscles supporting the joints without overstraining them. Exercise improves joint flexibility, range of motion, and muscle strength, providing better support for the joints and reducing the risk of injury.
- **Get Enough Sleep**: Adequate sleep reduces inflammation, which can irritate the tissues protecting the joints and ultimately lead to deterioration. Good sleep allows your body to repair damaged tissues.
- **Improve Sitting Posture**: Sitting in a healthy position helps prevent pressure on the joints, especially in the spine, neck, and shoulders. Good posture distributes body weight evenly and reduces joint stress. When sitting at your desk, keep your back straight, shoulders back, and maintain a 90-degree angle at the hips and knees.
- **Manage Stress**: Chronic stress can exacerbate inflammation and joint pain, so it’s essential to dedicate at least an hour daily to relaxing activities, including meditation, yoga, or deep breathing.
- **Listen to Your Body**: If a particular activity causes pain, you need to stop doing it and rest, as ignoring these signals can lead to more severe joint damage.