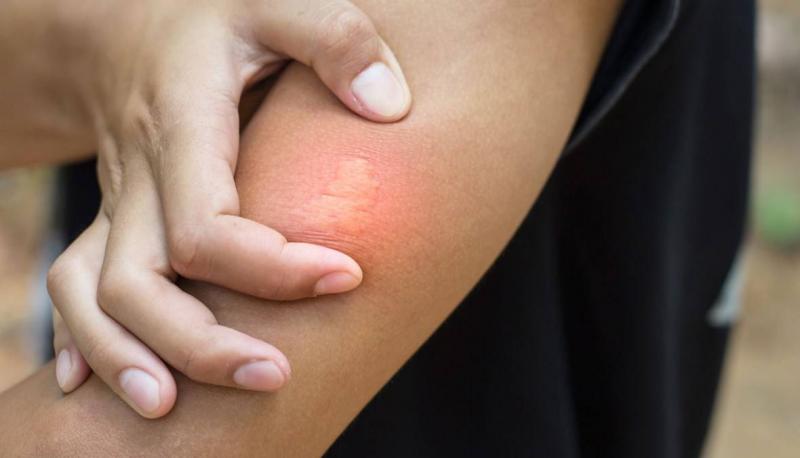
Bee stings are common risks one may face during the summer, and they usually do not pose a serious threat. However, there are cases where bee stings can lead to death due to allergic reactions in some individuals, according to Medisite.
When Can One Be Stung by a Bee?
Every year, millions are stung by bees, which are found everywhere and are more likely to sting during the summer. It is known that female bees release venom, particularly those that sting are the social bees living in colonies. This type of bee is more aggressive than solitary bees. When approaching these groups, the bees sting to protect their colony. Despite millions being stung annually, there are dozens of recorded fatalities.
What Are the Symptoms of a Bee Sting?
Typically, the effects of a sting are local and mild, causing:
- Sharp and immediate pain
- Itching
- Swelling
- Redness
However, if a sting occurs on the face, mouth, tongue, or throat, swelling can increase to the point of obstructing the airways, which becomes more serious and requires immediate medical intervention. If multiple stings occur, the effects may prolong due to the excess venom entering the body. General symptoms may include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Elevated body temperature
- A feeling of malaise
- Headaches
In cases of allergic reactions, symptoms vary from case to case. An allergic reaction to a bee sting is considered when the local effect is significantly worse compared to typical cases, where swelling exceeds 10 centimeters and may involve surrounding joints that also appear swollen. Symptoms that may occur at this point include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Severe confusion
- A feeling of constriction in the heart
- Anaphylactic shock, which can lead to cardiac arrest
Therefore, it is essential for those at higher risk of allergies to be cautious during this season to avoid bee stings.
How Long Can Symptoms and Effects Last?
If the effects of the sting are normal without causing an allergic reaction, they will subside within no more than 24 hours.
What Should Be Done in Case of an Allergy to Bee Stings?
Individuals who are allergic to bee stings should keep an emergency and first aid kit readily available, which can be obtained through a prescription following a previous similar incident. This kit should include an antihistamine to take upon being stung, a medication containing corticosteroids if the effects of the sting spread, and an adrenaline injection to use immediately in case of an allergic reaction that causes difficulty in breathing, itching all over the body, nausea, and chest tightness. For those who do not know they have this condition, it is important to seek help as soon as the first signs appear.